Since its inception, we have tried different materials for plumbing pipes, and technology has only made it better over time. In the ancient days, people used clay pipes to deliver clean water. The first known example of when clay pipes were used for plumbing dates to 4000 BCE in Babylonia. This is often considered the birthplace of urban plumbing.
Today, the choice comes down to two main types: plastic piping vs. metal piping.
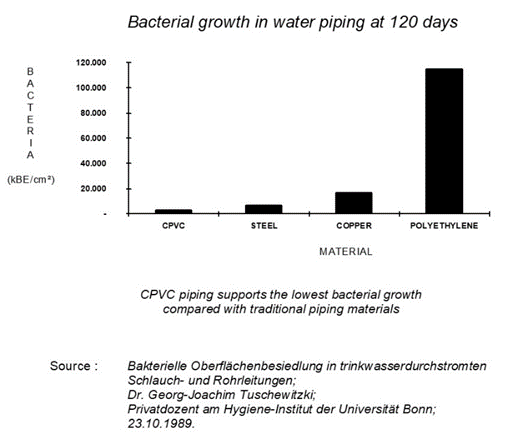
Among varied plastic piping systems today CPVC is the most preferred plumbing pipe in Hot & Cold-water applications.
CPVC fittings and pipes have several advantages over metal pipes, today CPVC has evolved as the No 1 choice for as plumbing piping system in India.
CPVC stands out as the superior choice over metal piping materials with properties that ensure a longer lifespan, consistent water quality, safety, and efficiency. Let’s take a look at a few of the many advantages of CPVC pipes and understand what makes them your best choice:
Corrosion Resistance: One of the biggest drawbacks of metal piping, especially GI pipes, is its susceptibility to corrosion. Over time, metal pipes can rust and degrade, leading to leaks and water contamination. CPVC due to its inert nature doesn’t react with the dissolved particles in water hence inherently resistant to corrosion, ensuring a longer lifespan and cleaner water supply.

Scaling Resistance: Water scale buildup is a concern with metal pipes, affecting water pressure and flow. CPVC pipes have smooth inner surfaces and also being inert in nature resist the formation of pipe scaling, thus maintaining consistent water pressure and extending the system’s efficiency. In Hazen William’s - the higher the C factor number, the smoother the pipe’s inner surface. At the origin, GI has a C factor of 120, and CPVC and PEX are around 150. This denotes that the flow rate in CPVC on the day of installation is better than GI and will remain the same due to no scale or corrosion buildup. However, in GI, the C factor of 120 will reduce to 100 or even lower due to corrosion & scale build-up with the passage of time.
Installation Ease and Cost: Metal pipe installation can be labour-intensive and costly, often requiring specialised skills for welding and fitting. CPVC piping system, on the other hand, is lightweight compared with metal pipe weight, thus is easy to install. The process of solvent CPVC welding is straightforward which significantly reduces labour time and installation costs.
Joint Welding: CPVC uses solvent welding to create strong and leak-proof joints. This is also termed the cold fusion process. The joining process is so simple that even common people can easily do a CPVC joining of their own. Unlike metal pipes, it does not require any special tools for joining. A plumber requires a pipe cutter, a solvent cement a chamfering tool for welding the CPVC piping system.
Pipe Weight: When compared to the metal counterparts, CPVC pipe weight tends to be considerably lighter. This further reduces the transportation costs and simplifies the handling process during installation, making CPVC an attractive option for projects of all sizes.
Fabrication Flexibility: Unlike metal piping that may require prefabrication, CPVC pipes can be easily cut and customised on-site. This adaptability allows for last-minute changes and adjustments without significant delays or additional costs.
Fire Safety: CPVC piping is fire resistant, meaning it is designed to perform better in fire conditions compared to some metal pipes. CPVC does not support combustion which further adds an extra layer of safety to the buildings.
Superior Insulation: CPVC due to its lower thermal conductivity properties results in reduced heat loss. Hence insulation costs are very low in CPVC piping systems. Metal pipes on the other hand require heavy insulation on hot water lines resulting in higher insulation costs.
Cost Efficiency: Lower installation costs, minimal maintenance, and longer service life make CPVC a cost-effective solution for both residential and commercial plumbing systems.
FlowGuard Plus CPVC pipes encapsulate all the aforementioned benefits and go a step further. Recognized for their superior quality, these pipes ensure reliability and safety for hot and cold-water applications. With FlowGuard Plus, you’re not just choosing CPVC piping; you’re opting for a system that promises:
Building an efficient plumbing system requires the right materials and tools. Today in India CPVC is the most preferred plumbing piping system for Hot & Cold-water systems. And if it is CPVC it has to be FlowGuard Plus as FlowGuard is the inventor of CPVC technology. FlowGuard offers unmatched quality, reliability & consistency in the market. Visit our website to learn more.
Which is better CPVC pipe or metal pipe?
In today's scenario, CPVC is always a better choice for plumbing applications due to its ease of installation, lightweight, hence ease of transport, no to corrosion, unaffected by chlorine in water, low thermal conductive properties, and negligible maintenance once installed properly.
How long do metal pipes last?
CPVC pipe materials are designed to have a service life of about 50 years for both hot and cold-water applications. GI pipes, on the other hand, can endure up to 50 years in rural areas with less pollution; however, in urban polluted regions, their lifespan decreases by 50%. On the other hand, CPVC pipe materials are designed to have a service life of about 50 + years for both hot and cold-water applications.
Can you connect CPVC pipe to metal pipe?
Yes, CPVC pipes can be connected to metal pipes using special Transition fittings, such as male or female adapters, in bigger diameter flanges are a preferred option. It can easily connect a variety of pipes, pumps, valves, etc., and piping of all materials can be joined using flanges, making them the most common mechanism for joining two different piping materials, especially in industrial processes.
Is metal pipe safe for drinking water supply?
Metal pipes, particularly copper and stainless steel, are safe for drinking water supply as they do not release harmful substances into the water. However, galvanised steel that can corrode may pose health risks and are not recommended for drinking water supply.
